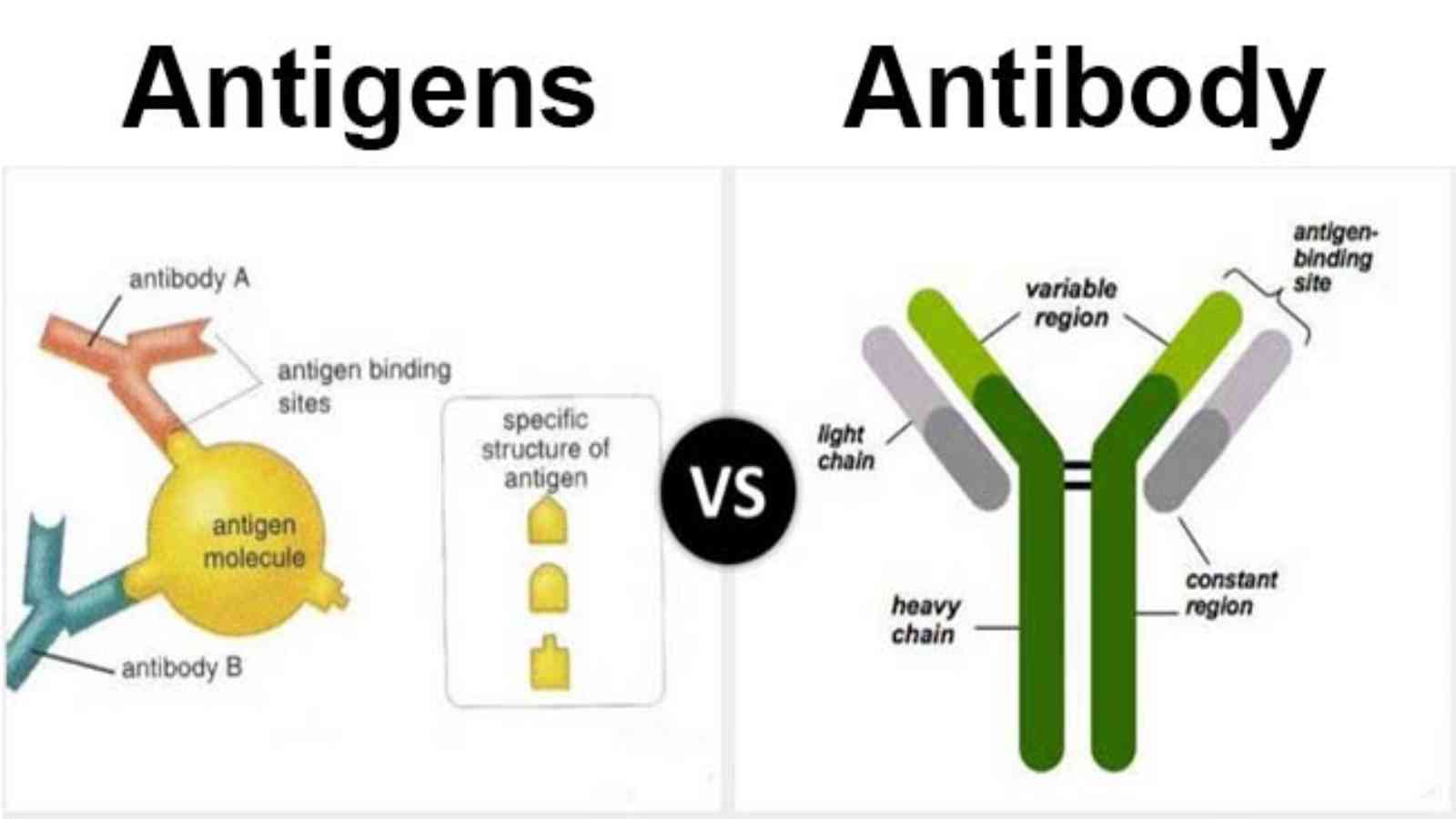
Antigens Microbiology . Antigen is a substance usually protein in nature and sometimes polysaccharide, that generates a specific immune response and induces the formation of a specific antibody or specially sensitized t cells or both. an antigen is a molecule or particle, often found on the surface of cells, viruses, or bacteria, that triggers an. an antigen is defined as a substance that reacts with antibody molecules and antigen receptors on lymphocytes. an antigen is a substance or an element that has the ability to induce an immune response.
from www.eduvast.com
Antigen is a substance usually protein in nature and sometimes polysaccharide, that generates a specific immune response and induces the formation of a specific antibody or specially sensitized t cells or both. an antigen is defined as a substance that reacts with antibody molecules and antigen receptors on lymphocytes. an antigen is a substance or an element that has the ability to induce an immune response. an antigen is a molecule or particle, often found on the surface of cells, viruses, or bacteria, that triggers an.
Difference Between Antigen and Antibody
Antigens Microbiology an antigen is a substance or an element that has the ability to induce an immune response. an antigen is a substance or an element that has the ability to induce an immune response. Antigen is a substance usually protein in nature and sometimes polysaccharide, that generates a specific immune response and induces the formation of a specific antibody or specially sensitized t cells or both. an antigen is a molecule or particle, often found on the surface of cells, viruses, or bacteria, that triggers an. an antigen is defined as a substance that reacts with antibody molecules and antigen receptors on lymphocytes.
From philschatz.com
Polyclonal and Monoclonal Antibody Production · Microbiology Antigens Microbiology an antigen is a substance or an element that has the ability to induce an immune response. Antigen is a substance usually protein in nature and sometimes polysaccharide, that generates a specific immune response and induces the formation of a specific antibody or specially sensitized t cells or both. an antigen is a molecule or particle, often found. Antigens Microbiology.
From riset.guru
Difference Between Antigen And Pathogen In Tabular Form Ox Science Riset Antigens Microbiology Antigen is a substance usually protein in nature and sometimes polysaccharide, that generates a specific immune response and induces the formation of a specific antibody or specially sensitized t cells or both. an antigen is defined as a substance that reacts with antibody molecules and antigen receptors on lymphocytes. an antigen is a substance or an element that. Antigens Microbiology.
From www.studocu.com
Antigens General Microbiology Studocu Antigens Microbiology Antigen is a substance usually protein in nature and sometimes polysaccharide, that generates a specific immune response and induces the formation of a specific antibody or specially sensitized t cells or both. an antigen is a molecule or particle, often found on the surface of cells, viruses, or bacteria, that triggers an. an antigen is a substance or. Antigens Microbiology.
From www.mdpi.com
Antibodies Free FullText Applications of AntibodyBased Antigen Antigens Microbiology Antigen is a substance usually protein in nature and sometimes polysaccharide, that generates a specific immune response and induces the formation of a specific antibody or specially sensitized t cells or both. an antigen is a molecule or particle, often found on the surface of cells, viruses, or bacteria, that triggers an. an antigen is a substance or. Antigens Microbiology.
From www.eduvast.com
Difference Between Antigen and Antibody Antigens Microbiology an antigen is defined as a substance that reacts with antibody molecules and antigen receptors on lymphocytes. Antigen is a substance usually protein in nature and sometimes polysaccharide, that generates a specific immune response and induces the formation of a specific antibody or specially sensitized t cells or both. an antigen is a substance or an element that. Antigens Microbiology.
From www.sciencephoto.com
Antibodies and Antigens, Illustration Stock Image F031/8250 Antigens Microbiology Antigen is a substance usually protein in nature and sometimes polysaccharide, that generates a specific immune response and induces the formation of a specific antibody or specially sensitized t cells or both. an antigen is a substance or an element that has the ability to induce an immune response. an antigen is a molecule or particle, often found. Antigens Microbiology.
From www.mdpi.com
Micromachines Free FullText Lateral Flow Immunoassays for Antigens Microbiology Antigen is a substance usually protein in nature and sometimes polysaccharide, that generates a specific immune response and induces the formation of a specific antibody or specially sensitized t cells or both. an antigen is a molecule or particle, often found on the surface of cells, viruses, or bacteria, that triggers an. an antigen is a substance or. Antigens Microbiology.
From www.dreamstime.com
Antigens Vector Illustration. Labeled Antibody, Pathogen Educational Antigens Microbiology an antigen is a substance or an element that has the ability to induce an immune response. Antigen is a substance usually protein in nature and sometimes polysaccharide, that generates a specific immune response and induces the formation of a specific antibody or specially sensitized t cells or both. an antigen is a molecule or particle, often found. Antigens Microbiology.
From www.coursehero.com
Hypersensitivities Microbiology Course Hero Antigens Microbiology an antigen is a molecule or particle, often found on the surface of cells, viruses, or bacteria, that triggers an. an antigen is a substance or an element that has the ability to induce an immune response. Antigen is a substance usually protein in nature and sometimes polysaccharide, that generates a specific immune response and induces the formation. Antigens Microbiology.
From microbenotes.com
Antigen Properties, Structure, Types, Examples Antigens Microbiology Antigen is a substance usually protein in nature and sometimes polysaccharide, that generates a specific immune response and induces the formation of a specific antibody or specially sensitized t cells or both. an antigen is a substance or an element that has the ability to induce an immune response. an antigen is defined as a substance that reacts. Antigens Microbiology.
From www.thevaccinemom.com
The Beautiful Immune System Lesson 3 What is an Antigen? The Vaccine Mom Antigens Microbiology an antigen is a molecule or particle, often found on the surface of cells, viruses, or bacteria, that triggers an. Antigen is a substance usually protein in nature and sometimes polysaccharide, that generates a specific immune response and induces the formation of a specific antibody or specially sensitized t cells or both. an antigen is defined as a. Antigens Microbiology.
From www.britannica.com
Antibody Definition, Structure, Function, & Types Britannica Antigens Microbiology Antigen is a substance usually protein in nature and sometimes polysaccharide, that generates a specific immune response and induces the formation of a specific antibody or specially sensitized t cells or both. an antigen is a molecule or particle, often found on the surface of cells, viruses, or bacteria, that triggers an. an antigen is defined as a. Antigens Microbiology.
From microbenotes.com
B cell (B lymphocyte) Definition, Types, Development, Applications Antigens Microbiology an antigen is defined as a substance that reacts with antibody molecules and antigen receptors on lymphocytes. an antigen is a substance or an element that has the ability to induce an immune response. an antigen is a molecule or particle, often found on the surface of cells, viruses, or bacteria, that triggers an. Antigen is a. Antigens Microbiology.
From www.cell.com
ImmunoPCR a promising ultrasensitive diagnostic method to detect Antigens Microbiology Antigen is a substance usually protein in nature and sometimes polysaccharide, that generates a specific immune response and induces the formation of a specific antibody or specially sensitized t cells or both. an antigen is defined as a substance that reacts with antibody molecules and antigen receptors on lymphocytes. an antigen is a substance or an element that. Antigens Microbiology.
From labpedia.net
Human Leucocyte Antigen B27, Antigen (HLA B27 Antigens Microbiology an antigen is defined as a substance that reacts with antibody molecules and antigen receptors on lymphocytes. Antigen is a substance usually protein in nature and sometimes polysaccharide, that generates a specific immune response and induces the formation of a specific antibody or specially sensitized t cells or both. an antigen is a molecule or particle, often found. Antigens Microbiology.
From courses.lumenlearning.com
Antibody Functions Biology for Majors II Antigens Microbiology an antigen is a substance or an element that has the ability to induce an immune response. Antigen is a substance usually protein in nature and sometimes polysaccharide, that generates a specific immune response and induces the formation of a specific antibody or specially sensitized t cells or both. an antigen is defined as a substance that reacts. Antigens Microbiology.
From www.mdpi.com
IJMS Free FullText Immune Regulatory Functions of Macrophages and Antigens Microbiology an antigen is a molecule or particle, often found on the surface of cells, viruses, or bacteria, that triggers an. an antigen is a substance or an element that has the ability to induce an immune response. Antigen is a substance usually protein in nature and sometimes polysaccharide, that generates a specific immune response and induces the formation. Antigens Microbiology.
From courses.lumenlearning.com
Hypersensitivities Microbiology Antigens Microbiology an antigen is a molecule or particle, often found on the surface of cells, viruses, or bacteria, that triggers an. Antigen is a substance usually protein in nature and sometimes polysaccharide, that generates a specific immune response and induces the formation of a specific antibody or specially sensitized t cells or both. an antigen is a substance or. Antigens Microbiology.